
论文题目:Aqueous Al-N2 battery assembled by hollow molybdenum phosphate microspheres for simultaneous NH3 production and power generation
论文作者:Jintao Ren, Lei Chen, Haoyu Wang, Zhongyong Yuan*
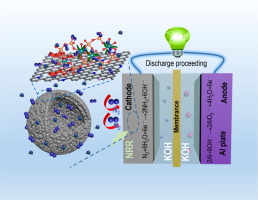
Abstract:
Developing controllable and facile devices beyond traditional N-2 electrocatalysis cell is critical for the commercial production of NH3 through electrochemical N-2 reduction reaction (NRR) under ambient condition. Herein, the aqueous Al-N-2 battery, fabricated by coupling the hollow molybdenum phosphate microspheres as cathode and the Al plate as anode within KOH electrolyte, was assembled for the electrochemical reduction of N-2 to NH3 and power generation during the discharge process. Benefiting from the desirable active components and the structural advantages, the hollow molybdenum phosphate microspheres derived from molybdenum phosphonates exhibit high NH3 yield rate of 18.66 mu g h(-1) mg(cat.)(-)1 with the Faradaic efficiency of 9.04% at - 0.2 V vs. reversible hydrogen electrode, associated with excellent robustness for cycling operation. The Mo4+ species of molybdenum phosphates are verified as the active components for NRR through the associative reaction pathway. When measured in the flow battery configuration with flowing N-2 during discharge, the formed Al-N-2 battery delivers the high NH3 yield rate of 13.47 mu g h(-1) mg(cat.)(-1) and Faradaic efficiency of 5.06% at 1.0 V vs. Al(OH)(4)(-)/Al, which can be stably maintained in discharge cycling tests over 20 cycles. Moreover, the peak power density of 2.37 mW cm(-2) and the long-term energy output are still achieved by this Al-N-2 battery during the discharge process. This work not only supplies some guidelines for the rational design of active NRR electrocatalysts from earth-abundant elements but also provides a reasonable and promising devices for efficient electrochemical N-2 fixation and power generation.