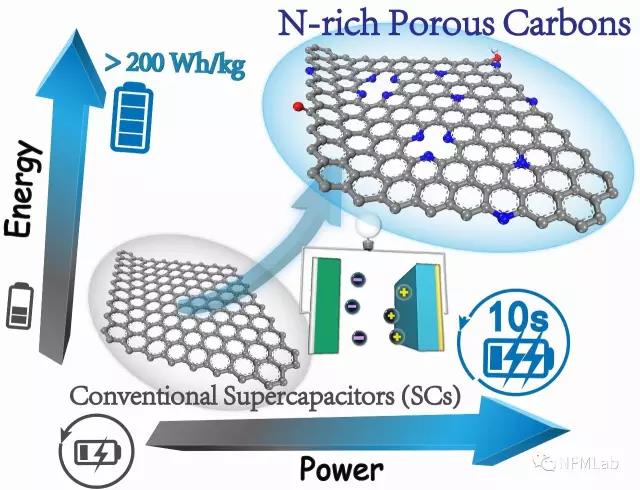
超级电容器具有快速充放电、长循环寿命和高安全性等优点,成为能源储存体系的研究重点,但一直难以突破其较低能量密度的瓶颈。氮掺杂能够对碳材料的导电性、孔结构和电化学活性位点进行调节,因而氮掺杂碳材料被认为是很有前景的超级电容器电极材料。尤其是近两年来富氮多孔碳材料在超级电容器领域取得了突破性进展,在保证大功率的前提下获得可媲美电池级别的高比能量。
南京理工大学杨梅博士与公司周震教授合作对富氮多孔碳材料在超级电容器中应用的储能机理、研究现状和发展方向等方面进行了阐述和总结。首先对碳材料中几种主要氮掺杂类型的结构特征和电子特性进行了分析,阐述了氮掺杂含量与导电性和孔结构之间的相互制约影响,并对其在不同电解液中的电化学行为进行了简单评述。同时,总结了富氮多孔碳材料对超级电容器比能量提升的促进作用,列举了其在水系非对称、新型对称到新兴非水混合体系中应用的相应突破性成果。最后对目前所存在的问题和挑战进行了系统总结,并对未来的研究方向提出了见解,对富氮多孔碳材料在超级电容器中的实际应用提供了指导。
Abstract:Featured with unique mechanical, electronic and chemical properties, nitrogen-doped carbon materials have become the research hotspot of energy storage. As electrode materials in supercapacitors (SCs), N-doped carbons have demonstrated intriguing flexibility and superb performances in a wide electrochemical window, equipped with versatile properties as both cathodes and anodes for constructing high voltage devices. Compared with limited doping level, N-rich and porous carbon materials (NPCs) are of great desire to release the restricted properties of N species and obtain high specific capacitances (>600 F g−1), pushing the energy density towards the battery level without scarifying the capacitor-level power ability. In this Research News we firstly discuss the key factors influencing the performance of NPC electrodes to disclose related charge storage mechanisms. In addition, the trade-off among N-content, porous structure and electrical conductivity is involved as well as electrochemical behaviors in different electrolytes. Also, various progressive developments are highlighted systematically ranging from asymmetric to symmetric and hybrid configurations, covering both aqueous and non-aqueous systems. Finally, some stubborn and unsolved problems are summarized, with prospective research guidelines on NPC-based SCs.