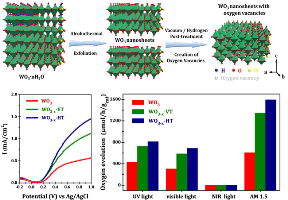
Substoichiometric tungsten oxide single-crystal nanosheets are successfully prepared via the exfoliation of layered tungstic acid and subsequent introduction of oxygen vacancies. The combination of different strategies, i.e., 2D-structure construction, the introduction of surface oxygen vacancies, and the creation of localized surface plasmon resonance can promote the light-harvesting performance of tungsten oxide through accumulative and synergistic effects.